Topic 1: Access Now Report on internet shutdowns
Context: India has had the most internet shutdowns for five years in a row now, recording almost half of all shutdowns globally in 2022, found a report.
Key details:
- The year also saw the highest total number of shutdowns around the world.
- Over 35 countries implemented shutdowns in 2022, compared with 25 in 2016.
- The Access Now report titled Weapons Of Control, Shields Of Impunity — Internet Shutdowns in 2022.
- India saw 84 shutdowns out of the total 187 worldwide.
-
Reasons for shutdowns:
- Protests, active conflicts, exams and elections were some of the triggers for the shutdowns worldwide.
-
Legal aspects:
- The proposed Draft Indian Telecommunication Bill, which would empower central and state governments with unrestricted powers to impose shutdowns signals the government’s intention to continue down this.
-
Indian telegraph act 1885:
- It includes temporary suspension of telecom services.
- Only the home secretary of the union or the state can issue such an order.
-
Section 144 CrPC:
- Under this provision the order can be issued by an officer of the rank of joint secretary or above, for shutting down internent services.
-
Section 69(A) of the information technology Act 2008:
- This provision gives the government power to block websites and not the internet as a whole.
Topic 2: The Great Pyramid of Giza
Context: A hidden corridor has been unearthed by scientists close to the main entrance of the 4,500-year-old Great Pyramid of Giza.
About the Pyramid:
- The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest of the three pyramids in Giza.
- Originally it is standing roughly 147 m above the Giza plateau.
- It is the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu.
-
Who built it?
- Construction was started in circa 2550 BC, during the reign of Khufu.
-
Significance:
- It was the tallest structure on the planet until the main spire of the Lincoln Cathedral in the United Kingdom overtook it in 1400 AD.
- The pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one to remain largely intact.
-
Tunnel system:
- There are two distinct tunnel systems inside the Great Pyramid:
- the Descending Passage (described by Greeks like Herodotus) and the
- Ascending Passage (more hidden, opened by the Arabs as recently as the 9th century).
- There are two distinct tunnel systems inside the Great Pyramid:
Topic 3: Pegasus
Context: In his recent lecture at Cambridge University, Congress leader alleged that the Israeli-made spyware Pegasus had been used to snoop on him.
About Pegasus
- Pegasus, developed by an Israel-based cybersecurity company .
- Initially it was thought that the spyware works only by sending an exploit link, and if the target user clicks on the link, the malware is installed on the user’s phone.
- Later it was revealed that Pegasus had evolved its method by using ‘zero-click attacks’, which do not require any action from the phone’s user.

The aftermath in India:
- The Supreme Court, in 2021, ordered an investigation headed by Justice RV Raveendran to conduct a thorough inquiry into the allegations.
- Two reports were submitted to the court, one by Justice Raveendran and another by a technical committee that analysed some of the phones allegedly targeted by Pegasus.
What do Indian laws outline?
-
Indian Telegraph Act:
- The Indian Telegraph Act, 1885 states that the Government can intercept a message or class of messages when it is:
- in the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India,
- thr security of the State,
- friendly relations with foreign states or public order or
- for preventing incitement to the commission of an offence.
- The Indian Telegraph Act, 1885 states that the Government can intercept a message or class of messages when it is:
-
Indian Telegraph Rules:
- Rule 419A was added to the Telegraph Rules in 2007 under which surveillance needs the sanction of the Home Secretary at the Central or State level, but in “unavoidable circumstance” can be cleared by a Joint Secretary or officers above, if they have the Home Secretary’s authorisation.
-
Section 69 of the Information Technology Act, 2000:
- It deals with electronic surveillance.
- It facilitates Government interception or monitoring or decryption of any information through any computer resource if it is in the interest of:
- the sovereignty or integrity of India, defence of India,
- security of the State,
- friendly relations with foreign States or
- public order or
- for preventing or investigating any cognizable offence.
Topic 4: Forest Certification in India
What is forest certification?
- Forest certification is a mechanism for forest monitoring, tracing and labeling timber, wood and pulp products and non-timber forest products where the quality of management from environmental, social and economic perspectives is judged against a series of agreed standards.
- It is a process that leads to the issuing of a certificate by an independent party, which verifies that an area of forest is managed to a defined standard.
- Forest certification refers to two separate processes viz.,:
-
forest management unit certification (FMU):
- Forest management certification is a process which verifies that an area of forest /plantations from where the wood, fiber and other non-timber forest products is extracted is managed to a defined standard.
-
chain of custody certification (COC):
- COC certification is a process of tracking forest products from the certified forest to the point of sale to ensure that product originated from a certified forest.
-
forest management unit certification (FMU):
Standards of forest certification:
- There are two major standards:
- one has been developed by Forest Stewardship Council, or FSC;
- the other by Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certifications, or PEFC.
- Both operate in India, but the Government is also working on its own national standards.
Forest certification in India
- The forest certification industry has been operating in India for the last 15 years.
- Currently, forests in only one state — Uttar Pradesh — are certified.
- The standards have been developed by the New Delhi-based nonprofit Network for Certification and Conservation of Forests (NCCF).
- The NCCF was set up in 2015 by representatives of forest-based industries, non-profits, forest auditors and government forest departments.
- Its aim is to set standards for certifying India’s forests, their products and their sustainable management.
India-specific standards
- India allows the export of only processed wood, not timber.
-
Why?
- The timber harvested from Indian forests is not enough to meet the domestic.
-
Trees outside forests:
- India’s forests contribute just about five million cubic metres of wood every year.
- Almost 85 per cent of the demand for wood and wood products is met by trees outside forests (ToF).
- About 10 per cent is imported.
- New certification standards are being developed for sustainable management of ToF.
Topic 5: World Bank’s Women, Business and the Law 2023 report
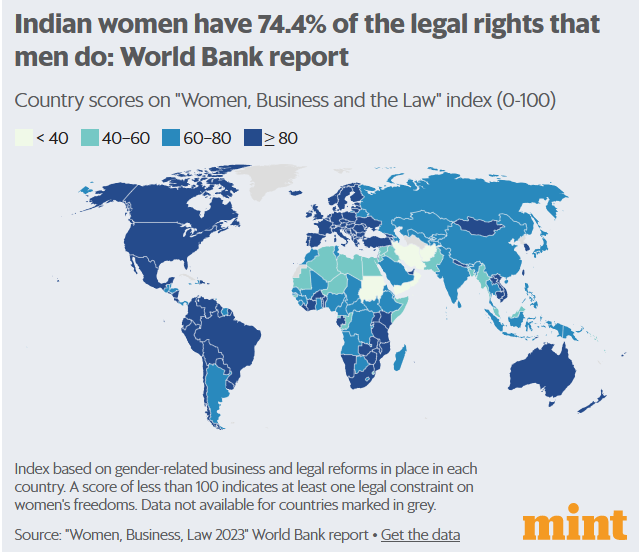
Context: The laws affecting the Indian working woman’s pay and pension do not provide for equality with Indian men, dragging India’s score in a World Bank index on the life cycle of a working woman down to 74.4.

Key details:
- A score of 100 on the Index means that women are on an equal standing with men on all the eight indicators being measured.
- India scored higher than the 63.7 average for the South Asian region, though lower than Nepal which had the region’s highest score of 80.6.
- For India, the Index used data on laws applicable in Mumbai, viewed as the country’s main business city.
- Score of India under the 8 indicators:

Indian reforms according the report
- In India the first observed reform occurred in 1987, when the country prohibited gender discrimination in employment in connection with recruitment, dismissal, transfer, training, and demotion.
- In 1994, two states in India, Karnataka and Maharashtra, reformed the Hindu Succession Act of 1956, equalizing inheritance rights for both sons and daughters and male and female surviving spouses.
- It was not until 2005, however, that India equalized inheritance rights across the country, through an amendment to the Hindu Succession Act of 1956.
- In 1997, the Supreme Court established the Vishaka Guidelines, a set of procedural guidelines for courts to use in cases of sexual harassment.
- The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act was passed in 2006
- The most recent reforms have included an increase in the duration of paid maternity leave
to at least 14 weeks in 2017. - In 2017, the state of Maharashtra eliminated restrictions on women’s ability to
work in jobs deemed to be dangerous. - In 2020, India established a social insurance system for the public administration of paid maternity leave benefits.
- Today, India receives a score of 100 on three indicators:
- Mobility,
- Workplace, and
- Marriage.

Topic 6: Pradhan Mantri-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission
Context: The World Bank is lending up to $1 billion to help India with preparedness for future pandemics as well as to strengthen its health infrastructure.
Key details:
- The lending will be divided into two complementary loans of $500 million each.
- Through this combined financing of $1 billion, the bank will support India’s flagship Pradhan Mantri-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM), launched in October 2021, to improve the public healthcare infrastructure across the country.
- One of the loans will prioritise health service delivery in seven States:
- Andhra Pradesh,
- Kerala,
- Meghalaya,
- Odisha,
- Punjab,
- Tamil Nadu,
- Uttar Pradesh.
-
The two loans:
- The $500-million Public Health Systems for Pandemic Preparedness Programme (PHSPP) will support the government’s efforts to prepare India’s surveillance system to detect and report epidemics of potential international concern.
- Another $500-million Enhanced Health Service Delivery Programme (EHSDP) will support government’s efforts to strengthen service delivery through a redesigned primary healthcare model.
- Both the PHSPP and the EHSDP loans have a final maturity of 18.5 years, including a grace period of five years.
Pradhan Mantri-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission
- It is one of the largest Pan-India health schemes for strengthening healthcare infrastructure.
- It was launched in 2021 to accomplish the vision of comprehensive healthcare across the country.
-
Aim:
- To fill the critical gaps in public health infrastructure, especially in critical care facilities and primary care in both the urban and rural areas.
-
3 major aspects:
- To strengthen grass root public health institutions to deliver universal comprehensive primary health care and critical care services.
- To expand and build an IT enabled disease surveillance system.
-
Expansion of research on COVID-19 and other infectious diseases and to develop the core capacity to deliver the One Health Approach to prevent, detect, and respond to infectious disease outbreaks in animals and humans.
- One Health is a collaborative, multisectoral, and transdisciplinary approach with the goal of achieving optimal health outcomes recognizing the interconnection between people, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
-
Components:
-
Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) Components:
- Ayushman Bharat – Health & Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) in rural areas
- Ayushman Bharat – Health & Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) in Urban areas
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs)
- Integrated District Public Health Laboratories in all districts
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks in all districts with a population more than 5 lakhs
-
Central Sector (CS) Components:
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks in 12 Central Institutions.
- Strengthening Surveillance of Infectious Diseases and Outbreak Response
- Strengthening Surveillance Capacities at Points of Entry
- Strengthening Disaster and Epidemic Preparedness
- Bio-security Preparedness and Strengthening Pandemic Research, National Institutions and Platforms for One Health
-
Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) Components:
-
Implementation Mechanism:
-
The CSS components will be implemented by following the existing framework, institutions and mechanisms of the National Health Mission.
- State Health Society and District Health Society established under National Health Mission (NHM) will be the implementing agency at the state and district level respectively.
- The National Health Systems Resource Centre (NHSRC) would provide technical support including for capacity building, on CSS components of the scheme.
-
The CSS components will be implemented by following the existing framework, institutions and mechanisms of the National Health Mission.
- The Central Sector components will be implemented by the central agencies/ subordinate offices/ autonomous bodies under the Department of Health & Family Welfare and the Department of Health Research, by following the existing procedure.
Need for Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission
-
Increasing government spending on health:
- India lags other developed countries in terms of healthcare infrastructure and manpower.
- To address this, the National Health Policy launched in 2017 highlighted the need to boost India’s public healthcare spending.
- India spent 1.8% of its GDP on public health expenditure in 2020–21.
- The government aims to increase the spending to 2.5% of the GDP by 2025.
-
To improve public access to healthcare:
- The government has introduced several schemes to make healthcare services more accessible and affordable to citizens.
- However there was still a shortfall of health centres in the remote areas of major states such as Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- The shortage of health subcentres stood at 23%, public health centres at 28% and community health centres at 37%.
Way forward:
- The healthcare infrastructure in India is expected to grow significantly and the size of the healthcare infrastructure market is projected to reach US$ 349.1 billion at 17% annually.
-
Increasing adoption of technology in the healthcare sector is radically transforming healthcare access and delivery in the remote areas.
- The Health Ministry’s eSanjeevani telemedicine service crossed 14 million teleconsultations.
- The Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission would not only help India build capabilities to effectively manage any emergency (e.g., COVID-19 pandemic), but also has the potential to create investment avenues, employment opportunities and contribute to the economic growth.
World BankThe World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects.The World Bank includes two institutions of the World Bank Group –the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) andInternational Development Association (IDA).It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference.The World Bank Group consists of:International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)International Development Association (IDA)International Finance Corporation (IFC)Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) |
Topic 7: Qualified Stock Brokers
Context: The National Stock Exchange (NSE) issued a list of 15 designated Qualified Stock Brokers (QSBs).
Who are Qualified Stock Brokers?
- QSBs are entities who, because of their size and scale of operations, can likely impact investors and the securities market, as well as governance and service standards.
- These stock brokers cater to the needs of a large number of investors.
- The failure of such stock brokers has the potential to cause disruption in the services they provide to large numbers of investors, causing widespread impact in the securities market.
-
Designation of QSBs:
- A stock broker will be designated as QSB on the basis of four parameters:
- number of active clients,
- total available assets of clients,
- trading volumes
- end-of-day margin obligations.
- All stock brokers with a total score greater than or equal to five on these four parameters are identified as QSBs.
- A stock broker will be designated as QSB on the basis of four parameters:
Topic 8: ADIP Scheme
Context: The Prime Minister of India has hailed the impact of Cochlear Implant Scheme where children up to the age of 5 years are operated free of cost.
What is a cochlear implant?
- The cochlear implant is a prosthetic device, a part of which is surgically implanted inside the cochlea.
- Cochlear implants have been found to be beneficial for children and adults with severe to profound hearing loss.
- While a hearing aid provides amplified sound energy to the ear, the cochlear implant directly provides electrical stimulation to the nerve endings in the cochlea.
Scheme of Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchase/Fitting of Aids and Appliances (ADIP Scheme)
-
Launched:
- The ADIP Scheme is in operation since 1981.
-
Aim:
- The main objective to assist the needy disabled persons in procuring aids and appliances that can reduce the effects of disabilities and enhance their economic potential.
- The aids and appliances supplied under the Scheme must have due certification.
- The scheme also envisages conduct of corrective surgeries.
- Grant-in-aid under the Scheme will not be given for commercial supply of aids/appliances.
-
Eligibility of the Beneficiaries
- He/she should be an Indian citizen of any age.
- Holds a 40% Disablement Certificate.
- Person who is employed/self-employed or getting pension and whose monthly income from all sources does not exceed Rs. 30,000/- per month.
- Persons who have not received assistance from the Government, local bodies and Non-Official Organisations during the last 3 years for the same purpose.
- However, for children below 12 years of age this limit would be 1 year.
Topic 9: Samarth Scheme
Context: It was informed in the parliament that 1.50 lakh persons were imparted skill (70% employed) under the Scheme.
Key details:
-
About the scheme:
- Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building in Textiles Sector) is a demand driven and placement-oriented umbrella skilling programme of Ministry of Textiles.
- The implementation period of the scheme is up to March 2024.
-
Aim:
- Samarth aims to incentivize and supplement the efforts of the industry in creating jobs in the organized textile and related sectors, covering the entire value chain of textiles, excluding Spinning and Weaving.
-
Implementation:
- The scheme is implemented through Implementing Partners (IPs) comprising of:
- Textile Industry/ Industry Associations,
- State government agencies and
- Sectoral Organizations of Ministry of Textiles like DC/ Handloom, DC/Handicrafts and Central Silk Board.
- The scheme is implemented through Implementing Partners (IPs) comprising of:
-
Features:
- It will follow the Aadhaar Enabled Biometric Attendance System with at least 80% of assessment.
- It has initiated a placement linked upskilling programme along with wage employment in the traditional sector (50%) and organised sector (70%).
- It will also continue tracking after placement for a period of one year.
- Samarth scheme will operate under a web-based Management Information System (MIS) that will monitor the total implementation process.
- A dedicated call centre with a helpline number.
-
Eligibility:
- Individuals have to be citizens of India
- Preference will be given to SC/ST, women, minorities, differently-abled persons, BPL category persons, and 115 aspirational districts (notified by the NITI Aayog).
Topic 10: Yellowstone National Park
Context: Yellowstone National Park, which celebrated its 151st anniversary, is widely considered to be the first national park in the world.
Key details:
-
Location:
- Yellowstone National Park is located in the western United States.
-
Established:
- It was established under the Yellowstone National Park Protection Act in 1872.
-
Significance:
- Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world.
- Yellowstone was designated a UNESCO biosphere reserve in 1976 and a World Heritage site in 1978.
-
Features:
- Over half of the world’s geysers and hydrothermal features are in Yellowstone
-
Yellowstone Lake is one of the largest high-elevation lakes in North America.
- It is centered over the Yellowstone Caldera, the largest supervolcano on the continent.
- The caldera is considered a dormant volcano.
- The most famous of all the geysers is Old Faithful.
